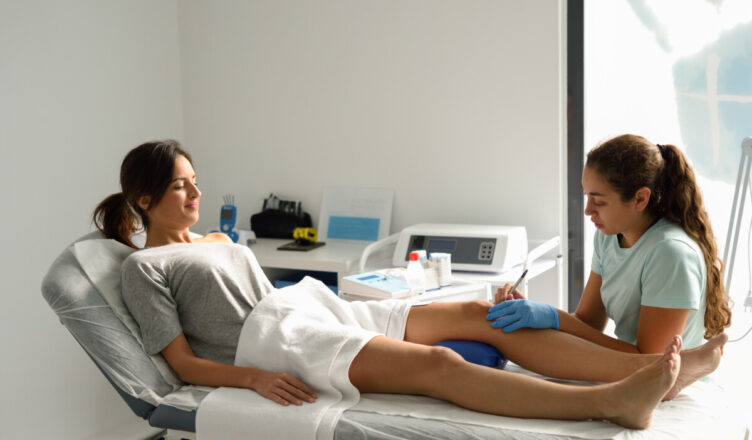
Neurotherapy, also called neurofeedback (NFB), EEG biofeedback, or brainwave training is a type of biofeedback that uses real-time displays of electroencephalography (EEG) to view and analyze brain activity. By recording brain wave activity using sensors placed on the patient’s head, a clinician can gather information about why the individual may be displaying clinical symptoms based on the brain. States of neurophysiological over-arousal or under-arousal can contribute to why a person may be showing symptoms of anxiety, depression, obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), attention deficit disorder (ADD), and a variety of other associated conditions.
Physical therapists who specialize in neurology work with a wide range of patients who may have the following conditions:
- Parkinson’s
- Stroke
- Multiple Sclerosis
Parkinson’s is a neurological disorder that affects people’s brain nerve cells. It’s a progressive disease that causes slurred speech, severe tremors and irregular facial expressions. Physical therapy has been shown to help those patients with chronic conditions. Treatment improves flexibility and strength and helps address the symptoms of Parkinson’s, such as gait, freezing and dystonia.
Stroke is a leading cause of disability in adults. Physical therapy includes constraint-induced movement therapy, functional electrical stimulation, motor image, partial body weight support and neuro therapy like biofeedback. Biofeedback is a type of neurological therapy that helps people be aware of how their muscles work and how they can change things. Treatment includes attaching electrodes to the patient’s skin to view muscle activity measurements on a screen.
With Multiple Sclerosis, it’s likely that the patient will be feeling weakness, fatigue and pain. Physical therapy helps patients with stretches to ease muscle spasms, exercises to keep muscles strong and specific range-of-motion exercises for movement. With treatment, patients improve balance problems and trouble moving their body.